What is Carotid Artery Disease?
Carotid artery disease occurs when the carotid arteries, which are responsible for bringing blood from the heart to the brain, become narrowed or obstructed due to plaque formation. This narrowing provides a risk of the plaque traveling to the brain and causing a stroke or mini-stroke.
RISK FACTORS
Increased age
Smoking history
High cholesterol
High blood pressure
Diabetes
Heart disease
Family history
SYMPTOMS
Stroke or “mini-stroke” (TIA)
- Loss of vision or blurry vision in one eye
- Weakness or numbness on one side of the body
- Slurred speech/difficulty speaking
- Facial drooping
TREATMENT OPTIONS
Risk factor modification
Medications
Exercise / lifestyle
Smoking cessation
Surgical intervention (carotid endarterectomy or stenting*)
*Only in select cases
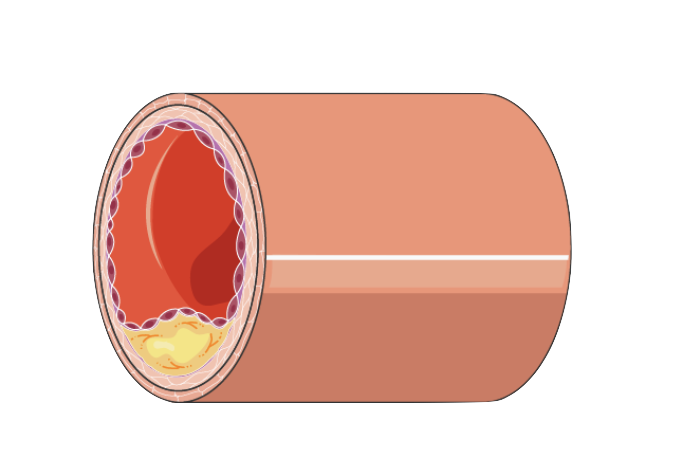
This is a graphic depicting the plaque build-up associated with carotid artery disease. In some cases, plaque can break off and travel to the brain, where it can directly occlude smaller branches of arteries, causing a mini-stroke or stroke.
DISCLAIMER
The information provided is for informational purposes only and is not to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis, treatment or care. Always seek the advice of a physician or other qualified health provider concerning any questions you may have regarding the above information and any medical condition you believe may be relevant to you or to someone else. The above information is not exhaustive and does not cover all diseases, physical conditions or their treatments.
