What is Chronic Venous Insufficiency and Varicose Veins?
Chronic venous insufficiency encompasses a spectrum of conditions related to the signs and symptoms that occur due to damage to the veins in the legs.
Damage to the one-way valves in the veins can occur due to obstruction in the case of deep vein thrombosis, valvular insufficiency in the case of varicose veins, or decreased contraction of the calf muscle surrounding the veins due to immobility. These changes cause blood to pool in the legs and put increased pressure on the walls of the veins.
Varicose veins are dilated superficial veins in the legs that appear as bulging blue protrusions under the skin. They are caused by damaged one-way valves in the veins that results in the backwards flow of blood. Over time, these veins become more prominent and torturous, causing both symptomatic and aesthetic concerns.
RISK FACTORS
Family history
Previous/current pregnancies
Occupations that involve standing (teacher, chef, cleaner, etc.)
Increased age
Sedentary lifestyle
History of blood clot in the legs
SYMPTOMS
Pain
Itching
Swelling
Burning
Leg fatigue
Heaviness
Skin discolouration
TREATMENT OPTIONS
Compression stockings
Exercise that uses the calf muscles (walking, heel raises, etc.)
Sclerotherapy/injections
Endovenous ablation (laser or cyanoacrylate adhesive)
Surgical stripping
Phlebectomy
Venoactive supplements
*your physician will discuss the most appropriate treatment options for you
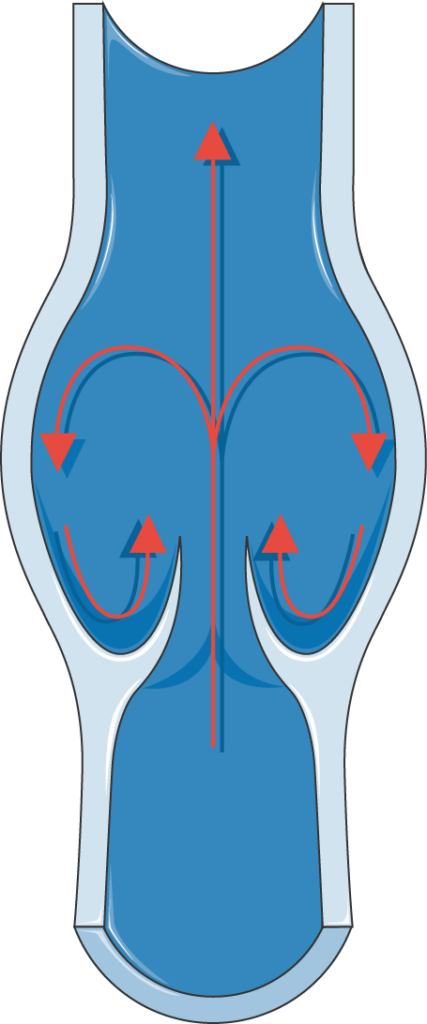
Incompetent valves cause blood to be pulled back down the vein with gravity, rather than returning upwards to the heart.
This added pressure causes the vein wall to expand and bulge out.
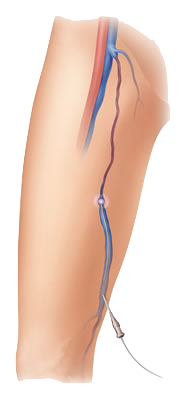
This diagram shows the process of EVLT treatment
- The laser is inserted into the vein of concern
- The fiber then emits a high intensity laser that heats up the vein
- This causes scar tissue production within the vein, consequently closing the vein
- This is continued down the entire length of the vein to seal it from the top to the bottom
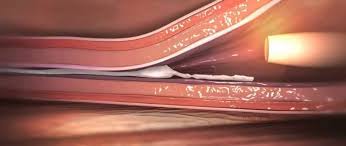
This is a cross section view of what the VenSeal ablation technique looks like
- A catheter is fed into the vein
- The VenaSeal device then dispenses medical grade adhesive (glue) to seal the vein
- This process is continued down the length of the vein
